Understanding Sustainability in Flex Packaging
June 2, 2023Single-Use Systems: Next Generation Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Solutions
Learn How Adopting Single Use Technology In Bioprocessing Industry Can Expedite Production And Cut Costs
Latest advancements in technology have enabled biotech and pharma companies to switch from traditional stainless steel systems to single use technology. This type of technology is experiencing tremendous growth in biopharma field as it is disposable and sterile while expediting production, increasing productivity, and reducing expenses.
Single-use systems are applied to all aspects of bioprocessing: from bioreactors, chromatography equipment, and mobile workstations, to sterilizing filters, fermenters, and single-use packaging (bags and tubing). And they are here to stay because they are a step forward from a rigid and slow-moving reusable system. In addition, single-use technology promotes sustainability by reducing water, energy and chemical consumption, which are otherwise used during sterilization of the equipment or products.
Jump to Section:
What Is a Single-Use System (SUS)?
The Origins Of Single-Use Systems In Biopharma Industry
Types Of Single-Use Products In Bioprocessing
The Most Common Materials Single-Use Systems Are Made Of
Single-Use Technology VS Stainless Steel In Biopharma
The Benefits: Why Switch To Single-Use Systems
Understanding the Potential Limitations of Single-Use Systems
The Environmental Factor
Final Thoughts: Single-Use Systems Boosting Biopharma Production To New Heights
Frequently Asked Questions
In this article, we will explain the basics of single-use systems in biopharmaceutical processing. We will explore some background information, draw a comparison with stainless steel manufacturing lines, and analyze its pros, cons and applications. By the time you read this article, you should have a better understanding of why switching to single-use systems pays off and why it makes bioprocessing agile and affordable.
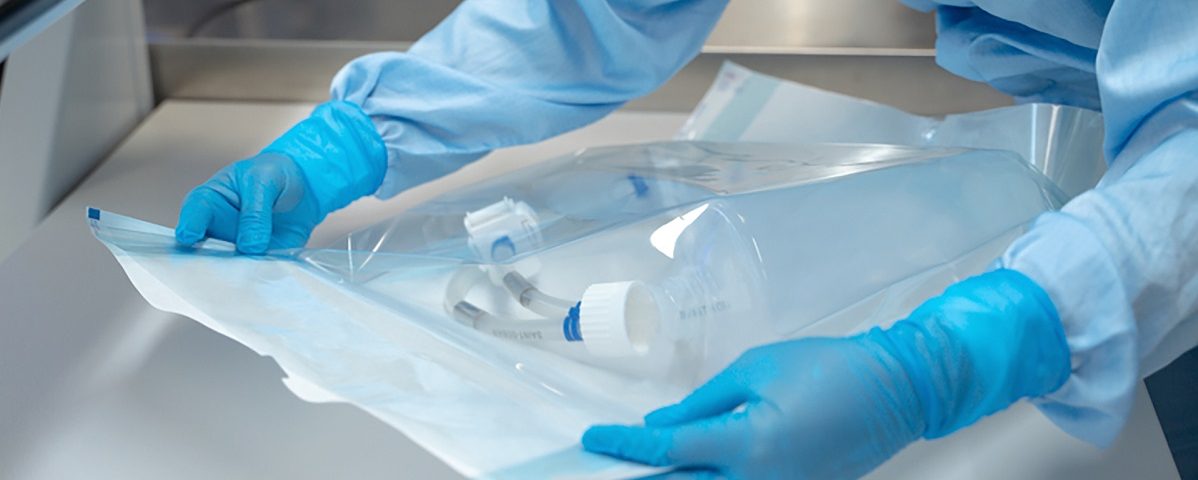
Pristine Clean Bags®: #1 Single-Use Bioprocessing Bags
Pristine Clean Bags and films have been utilized by the largest manufacturers in the single use systems and biopharma processing equipment for well over a decade. Our cleanroom bags and structures are at the forefront in protecting our customer’s single use systems and the accompanying accessories. Our packaging for single use systems is gamma stable for sterilization purposes. We continue to gain new customers in the single use system industry as a result of our consistent quality, our global supply chain and success with the largest companies in this space.
What Is a Single-Use System (SUS)?
In the past, the majority of bioprocessing tools ware reusable and made of stainless steel. What this means is that they had to be cleaned and sterilized within the production facility before and after every use. However, recent exponential growth of single-use technology has incrementally changed the way biopharmaceutical production works.
Single-use systems (SUS), also known as disposable bioprocessing equipment, are gaining lots of attention recently. They refer to biopharmaceutical equipment that is sterile and is intended to be used only once before being disposed of. SUS is typically made of plastic components which are later sealed and sterilized by gamma irradiation processes. For the most part, they are meant to be utilized in the same way as their reusable counterpart. Polymeric systems are primarily used as a substitute for stainless steel, since they do not have to be sterilized between different uses. They can simply be replaced, which maximizes flexibility, accelerates production, and reduces overall operating costs.
Before single-use systems were invented, biotech and pharma companies had to buy and store significant quantities of raw materials and products. Today, SUS has enabled biopharma to streamline manufacturing procedures by speeding up both scalability and research-to-production process, while mitigating risks. Single-use tools mainly facilitate customization and smooth integration of upstream and downstream bioprocessing.
The Origins Of Single-Use Systems In Biopharma Industry
Before the 1990s and the invention of disposable systems, when life science labs were required to move large amounts of serum, they had to reach for food industry bags made of plastic. And it didn’t take long before they started imitating this kind of container. Ultimately, this has led to the need for flexible single-use consumables. About a decade later, in the early 2000s, aseptic disposable systems were introduced. The introduction of disposable bioreactor was another breakthrough.
Biotech manufacturers became aware of remarkable advantages of single-use consumables for the pharma industry and gene therapy in particular. In the past two decades, lots of single-use facilities have been started, with a vast majority of pharma companies preferring disposable over traditional stainless steel bioreactors.
Today, modern single-use consumables are experiencing tremendous growth among the biopharmaceutical companies, bound to transform the majority of biomanufacturing processes.
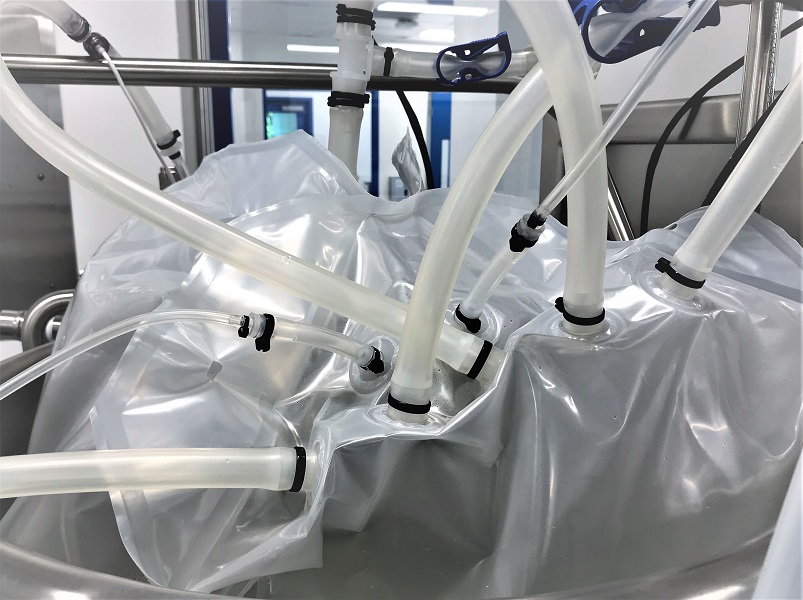
Types Of Single-Use Products In Bioprocessing
SUS has gained a lot of popularity in the biopharma industry, in both upstream and downstream processes. Some of the most common products using single-use systems are monoclonal antibodies (laboratory-made proteins), mRNA vaccines, and other pharmaceutical components made specifically for commercial market.
Instead of traditional systems, single-use systems have been successful in the following areas:
- Bioreactors
- Mixers
- Media bags
- Tubings
- Filter cartridges
- Bags
- Buffer containers
- Depth filters
- Connectors, clamps
- Chromatography
- Viral clearance
How Its Made: The Most Common Materials Single-Use Systems Are Made Of
Bioproduction by default, requires products and equipment with unique and specific attributes. Single-use technologies (SUT) are intended to be used only once, and they are typically made of different types of plastic such as:
- Polyamide – Commonly called nylon, this is a synthetic, low-density material with high thermal stability.
- Polyethersulfone – Plastic that can withstand high temperatures over long periods of time.
- Polypropylene – Complex, durable thermoplastic with good impact strength.
- Polytetrafluorethylene – A strong, nonflammable synthetic compound of fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene.
- Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) – Copolymer of vinyl acetate and ethylene.
- Polyethylene – The most common type of plastic used for packaging (clear films and bags).
- Cellulose acetate – A type of hard plastic compound made from the acetate ester of the plant substance cellulose.
- Polycarbonate – Transparent, strong, and tough thermoplastic polymers created with carbonate groups.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) – High-strength plastic compound resistant to heat and moisture.
Single-Use Technology VS Stainless Steel In Biopharma
Deciding whether to switch from traditional reusable stainless steel equipment to modern single-use is not always simple. Multiple aspects have to be considered and analyzed in order to make the right choice and decide which type is the most suitable for your line of work.
Single-use systems have become widely accepted due to their application in life science production. With diverse benefits over stainless steel, they have been widely used in clinical trials (cell and gene therapy).
Ready To Use
One of the main benefits of single use manufacturing systems over stainless steel is that SUS is sterile, so cleaning, sterilization, and validation of sterilization can be avoided. This saves not only resources but also precious time which can be used for other processes.
Increased Facility Flexibility
Single use technologies alleviate the need for complex infrastructure such as steam, plumbing, and WFI installation throughout the facility, which saves both time and the initial investment.
Streamlined Procedures
By being already sterilized and ready-to-use, SUS have a considerably quicker turnaround time, thus speeding up the manufacturing and deployment phase. Faster time from creation to market results in higher yields within the same timeframe.
Cost Savings
With disposable consumables, you will reduce operating costs for high utility bills, equipment, and specific infrastructure in the plant.
Large Scale Manufacturing
Since SUT is still in developmental stage for certain applications like large-scale manufacturing, stainless steel is a better option that is already well established.
The Benefits: Why Switch To Single-Use Systems
There are numerous advantages for implementing single-use systems into the developmental and manufacturing stage of life sciences, biotech and pharmaceutical industries. Some of the benefits include:
- Faster production process (accelerated turn-around time)
- Time saving (faster time to market)
- Increased flexibility (requires less space)
- Mitigated cross-contamination risks (sterilized using gamma radiation)
- Minimized cleaning
- Agility and scalability
- Reduced production costs (less instrumentation demand)
- Resource savings (water, energy, cleaning supplies)
- Easily integrated into the existing traditional multiuse systems
- Ready-to-use, fully sterilized
- Adaptable for specific applications
Understanding the Potential Limitations of Single-Use Systems
Even though the advantages are countless, there are still several potential hurdles in single-use systems for biopharma:
- Potential breakage of bags and loss of product material
- Multiproduct facility issues
- Limited downstream solutions
- Posing risks (leachables and extractables)
- Regulatory inspections
- Rigorous change management procedures
- Lack of interoperability
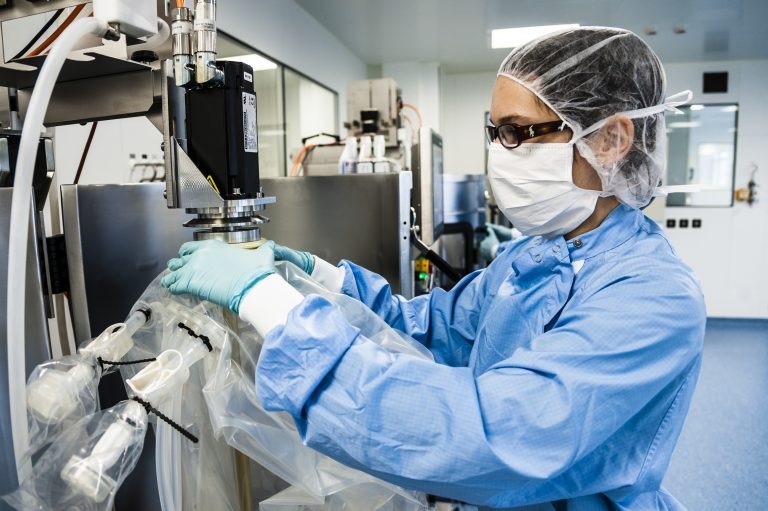

The Environmental Factor
In contrast to a popular opinion that reusable technologies are more sustainable, recent studies have shown that switching to SUS adds to more conscious and sustainable manufacturing due to:
- Water conservation (recycling water used in production)
- Decreased energy consumption (utilization of solar power)
- Smaller CO2 emissions
- Energy-efficient manufacturing technology
- Film downgauging
- Optimized transportation routes and low-emission vehicles
- Waste management and recycling production
- Ongoing research and development of environmental standards
Final Thoughts: Single-Use Systems Boosting Biopharma Production To New Heights
Single-use systems have significantly risen in popularity due to fast acceptance and implementation by life science companies. They mitigate contamination risks and help save money and time, while remaining compliant with high industry standards. Furthermore, operating costs are reduced, and productivity is increased significantly. It is safe to say that single-use technology will continue to develop and grow in both upstream and downstream production stages of bioprocessing for the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is single-use technology in biomanufacturing?
Single-use technology refers to sterile products and consumables intended to be discarded after one use. Since they do not need to undergo time-consuming cleaning and sterilizing procedures, they are often the preferred choice in biomanufacturing. With SUT, researchers and scientists can develop small enough quantities of a drug, suitable for testing in the preclinical and post-clinical stages.
What is a single-use component?
Single-use components represent a part of a single-use system that is used with the supply chain of biopharma. Single-use components that are pre-sterilized can be used in various stages of biopharmaceutical manufacturing process, such as production, packaging, storing and transportation.
How to determine whether switching to a single-use technology is the right choice?
When determining whether to switch from traditional to a modern, disposable system, try to take into consideration the following:
- Whether existing supplies and products are available
- Project deadline and budget
- Potential future replication needs


